
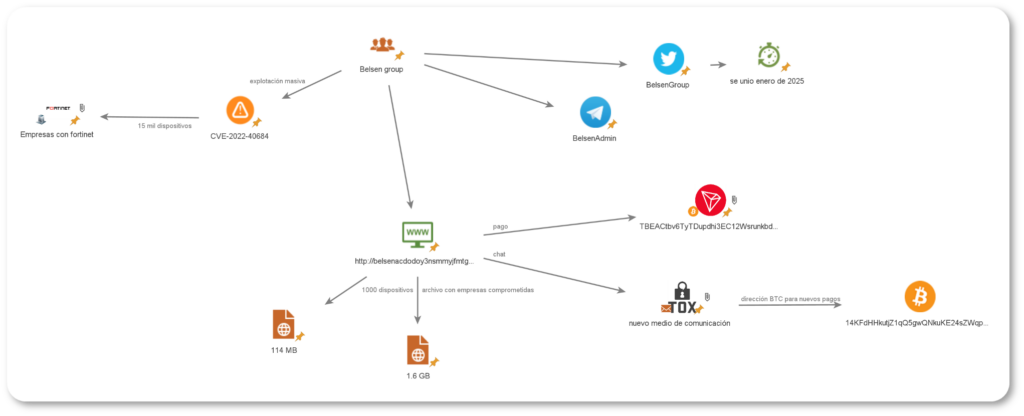
The team Cattleya has identified a new threat in the cybersecurity landscape: the Belsen group has leaked critical data from over 15.000 Fortinet devices after exploiting a high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2022-40684, CVSS 9.6).
The most alarming aspect of this incident is that the attackers compromised these devices back in 2022, before the vulnerability was patched, and waited over two years before making the breach public on the Deep Web forum.
Incident Timeline
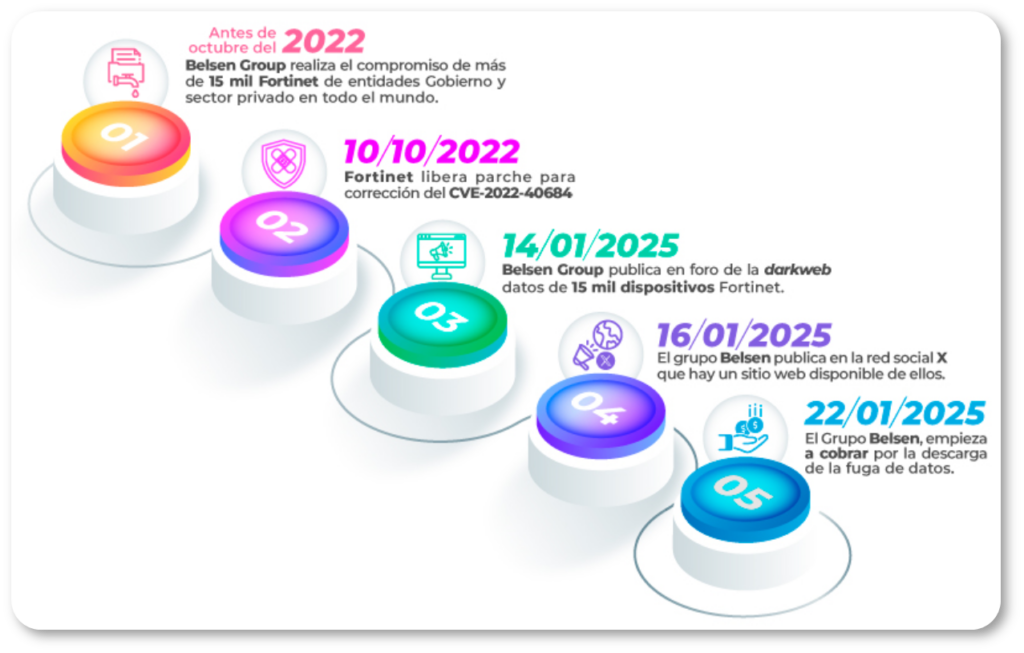
Before October 2022
The exact date when the Belsen Group discovered and began exploiting the Fortinet vulnerability remains uncertain. However, it has been confirmed that the compromise occurred before October 2022 affecting over 15,000 systems worldwide,impacting both public and private sector organizations.
October 10, 2022
Fortinet officially released a patch for vulnerability CVE-2022-40684, classified as critical with a CVSS score of 9.6.
🔗 Source: Fortiguard – FG-IR-22-377
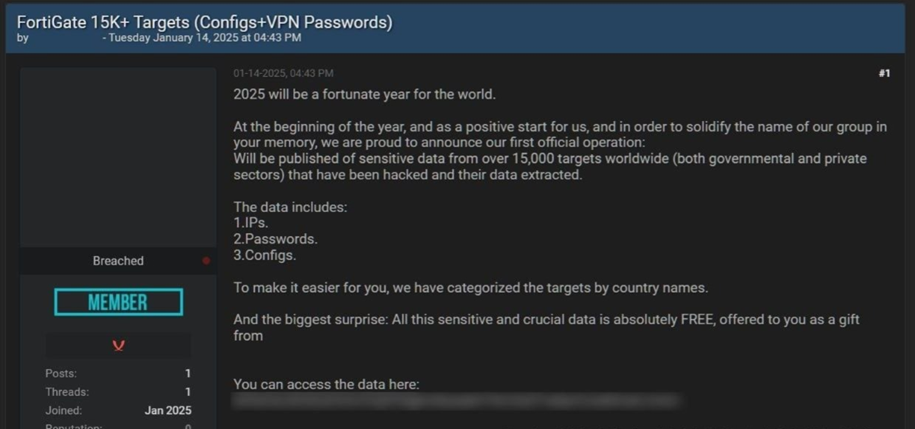
January 14, 2025
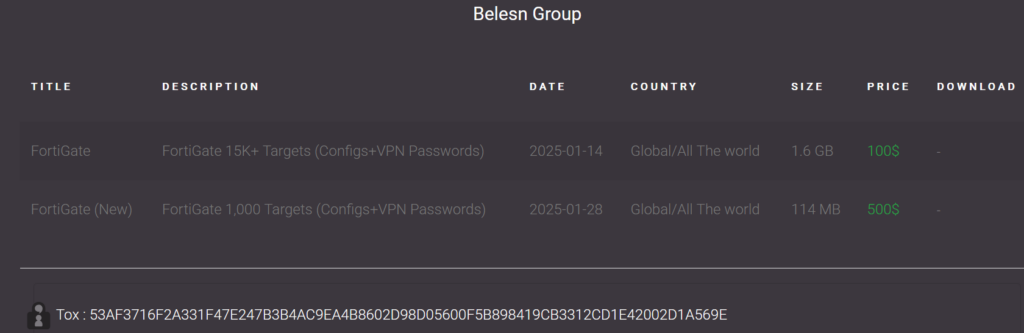
More than two years after the initial exploitation, the Belsen Group appeared on a clandestine Deep Web forumoffering a 1.6 GB file containing confidential information extracted from the compromised Fortinet devices. The file includes:
- Device configurations.
- VPN credentials and other sensitive data.
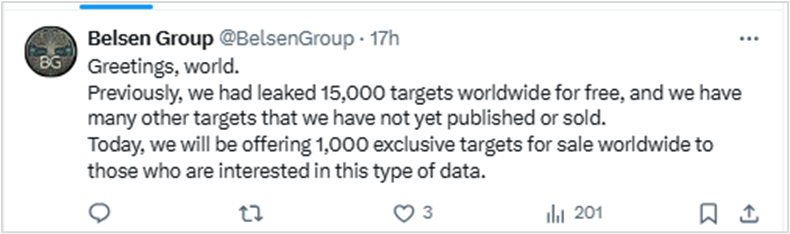
Two days later, Belsen Group published an announcement on X (Twitter), and launched a Tor network site to commercialize the leaked data.
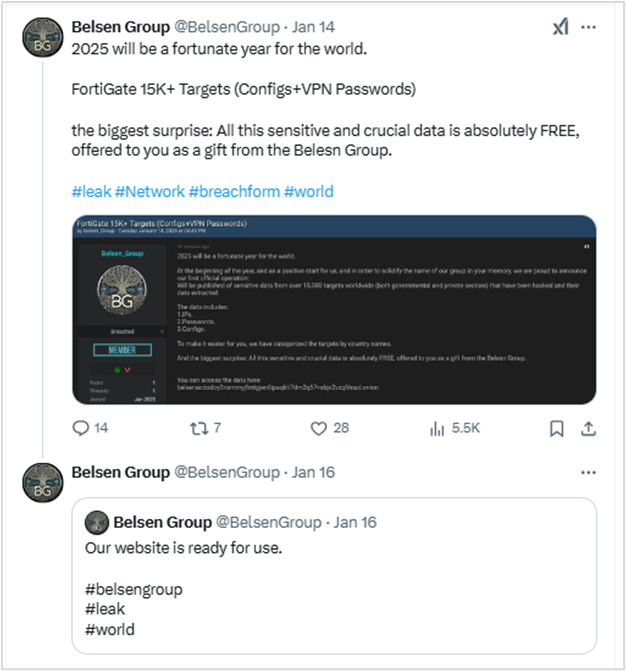
Six days after the leak, the Belsen Group announced they would charge $100 USD for downloading the file containing the compromised data.
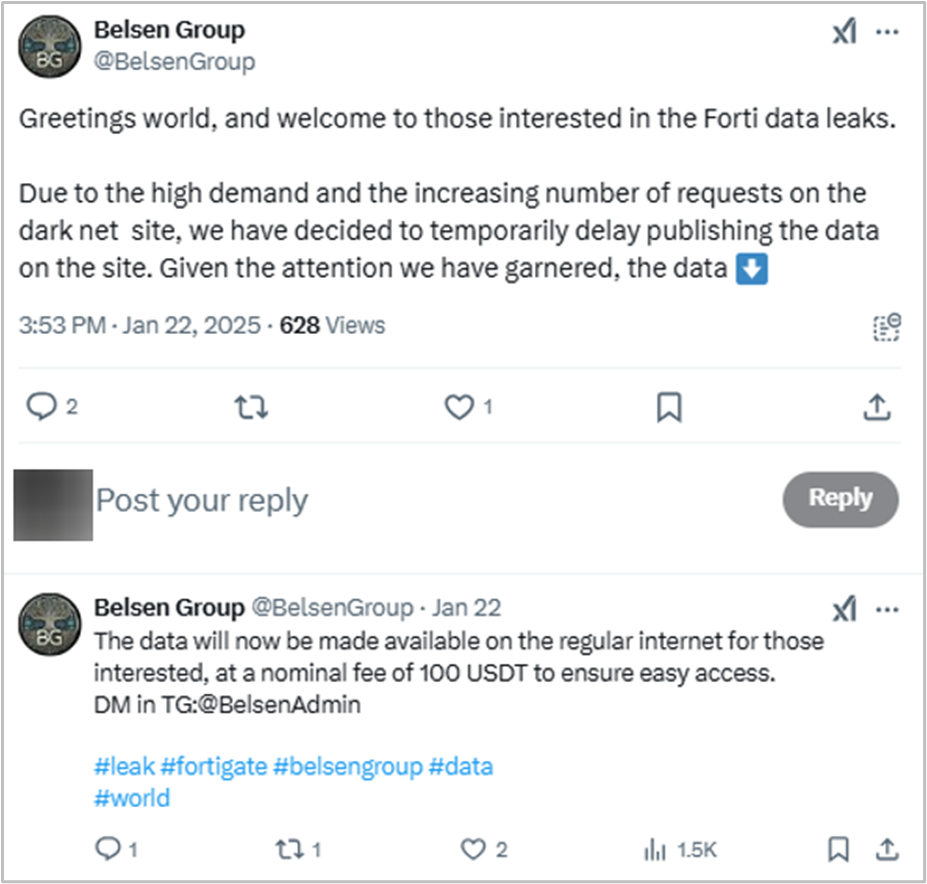
Additionally, an analysis of the website, reveals that users are required to make a $100 payment before downloading the information..

28 January 2025, Belsen Group releases a new batch of 1,000 additional devices for sale at 500 USD.
Threat Actor Information Identified by the Cattleya Cyber Intelligence Team Cattleya:
Impact
As part of the capabilities of proactive monitoring and warning early on of Cattleyathe team accessed and analyzed the leaked data, confirming a total of 15.474 different IPs , Each compromised system had a corresponding folder containing: Device configuration files, User credentials, Digital certificates for each device. Cattleya clients that were potentially affected were immediately notified. However, an analysis of the configurations and credentials by country revealed significant details about the impacted devices:
- 🇨🇴 Colombia: 372 compromised devices
- 🇲🇽 Mexico: 1,382 compromised devices
- 🇨🇱 Chile: 8 compromised devices
- 🇵🇪 Peru: 104 compromised devices
- 🇦🇷 Argentina: 245 compromised devices
These numbers highlight the severe impact of the breach across Latin America, affecting both private companies and government entities.
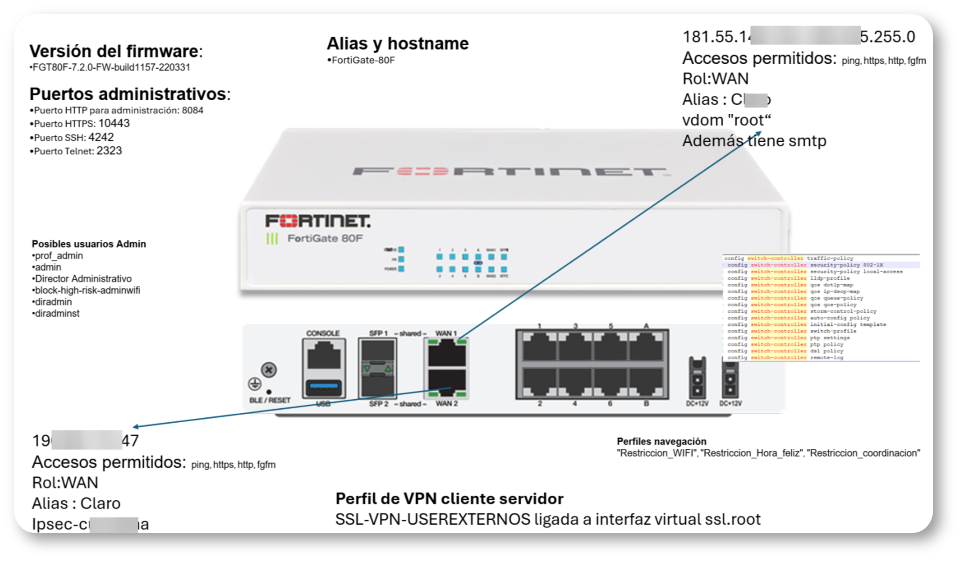
In an internal analysis, the Cattleya team conducted a reverse engineering assessment on a random configuration file to determine the extent of Belsen Group 's access and how other malicious actors might exploit this leaked data.
The leaked files expose organizations to serious risks, including:
- Access to private configuration settings
- Extraction of VPN credentials and authentication data
Identification of firmware versions, hostnames, and system configurations. - Compromised administrator emails and access permissions.
- Analysis of firewall rules and browsing profiles..
- Downloadable digital certificates from affected devices.
Since Belsen Group had access to this data since 2022, affected organizations should assume that:
- Attackers may have modified configurations and created hidden admin accounts.
- Persistent threats may still exist within compromised systems.
- Fortinet's patch does not mitigate prior intrusions if attackers already had internal network access.
Lessons Learned & Recommendations
This incident underscores the importance of:
- Proactive monitoring: Not only monitoring external attack surfaces, but also tracking underground forums and data leaks, as performed by Cattleya's leak detection module.
- Patching Alone Is Not Enough: Keeping systems up to date does not guarantee they weren’t previously compromised.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This should be a mandatory security standard in any critical environment.
- Configuration Audits: Organizations must regularly review devices for unauthorized access and suspicious changes.

If you want to check if your company is affected by this or other data breaches, Cattleya offers a ≫15-day Demo so you can explore the product's capabilities.



